Audits of training organisations are carried out on the basis of documents or on site, by 145 agents spread across the 18 regional audit services (SRC /DREETS).
Non-compliance may lead to sanctions imposed by the regional prefect or the minister, based on reports and observations.
Below are the most common non-conformities identified in the latest report, along with solutions to ensure compliance.


Training organizations must adhere to strict rules regarding communication and advertising. This includes:
• Avoiding misleading claims about qualifications, certifications, or accreditations.
• Including required legal information (e.g., registration number, Qualiopi certification if applicable).
• Avoiding misleading promises (e.g., guaranteeing full financial support when conditions apply).
• Check that your communication materials (website, brochures, social media) include your registration number (N.D.A.: Numéro de Déclaration d’Activité) and relevant certifications.
• Whenever you quote your N.D.A. in any communication, make sure that it includes the indication: “Cet enregistrement ne vaut pas agrément de l’État” (This registration does not imply State approval).
• Be precise and factual when describing your training programs.
• Add a disclaimer stating that financial support from funding bodies (OPCO, Pôle emploi) is subject to eligibility criteria.


Training organizations must keep their financial records separate from other business activities.
• Open a dedicated bank account for your training activity.
• Use accounting software that allows you to track income and expenses separately for each activity.
• Ensure that invoices and quotes for training services specify the legal framework for VAT exemption.
For example, if you are certified (by the DREETS, or previously DIRECCTE) exempt from VAT for your professional training activities, then all invoices for these VAT-exempt activities should include the following statement: “exonérée de TVA — Art. 261.4.4 a du CGI.”
If the invoice is for an activity other than for your VAT-exempt activity (for example, for translation work), and if this ‘extra’ activity does not exceed the threshold in turnover for application of VAT, then your invoices for this activity should include the following statement: “TVA non applicable selon l’article 293B du CGI.”


Not delivering a planned training session or failing to adhere to its content is a major cause of non-compliance.
• Create a detailed syllabus and schedule for each training program.
• Maintain attendance sheets signed by participants.
• Archive training materials and certificates of completion.
• If a session is cancelled, promptly notify participants and provide alternative solutions (rescheduling, refunds, etc.)


The ‘règlement intérieur’, or ‘internal regulations’, are mandatory for training programs exceeding 500 hours per year.
• Draft internal regulations that outline:
• General operating conditions.
• Rights and responsibilities of trainees.
• Safety and disciplinary rules.
• Ensure trainees sign the regulations before starting the training.


Training services must align with the legally defined categories (e.g., vocational training, skills assessments, validation of prior experience, apprenticeships).
• Verify that your programs fit within the legal framework for training services.
• If offering coaching, ensure it is integrated into a structured training program with clear learning objectives.


Trainees must receive clear and complete information about the training program, including objectives, content, and conditions.
• Provide a detailed syllabus before enrolment.
• Clearly state prerequisites and learning objectives.
• Supply a welcome booklet outlining the training process.


Any training commitment must be formalized through a contract or agreement.
Always issue a training contract specifying:
• The nature and duration of the training.
• Cost and funding arrangements.
• Responsibilities of both trainer and trainee.
 How to Conduct a Compliance Review
How to Conduct a Compliance Review
1. Review your administrative documents
• Ensure your registration number is valid.
• Verify the existence and compliance of your internal regulations.
• Update contract and agreement templates.
2. Check your accounting obligations
• Maintain separate financial records for training activities.
• Justify VAT exemption where applicable.
3. Assess your communication practices
• Ensure your advertising complies with legal requirements.
• Provide transparent information on training courses.
4. Evaluate your training procedures
• Ensure each training program has a structured syllabus.
• Keep records of attendance, training materials, and completion certificates.
5. Ensure traceability of your actions
• Retain essential documents (contracts, agreements, proof of attendance, etc.)
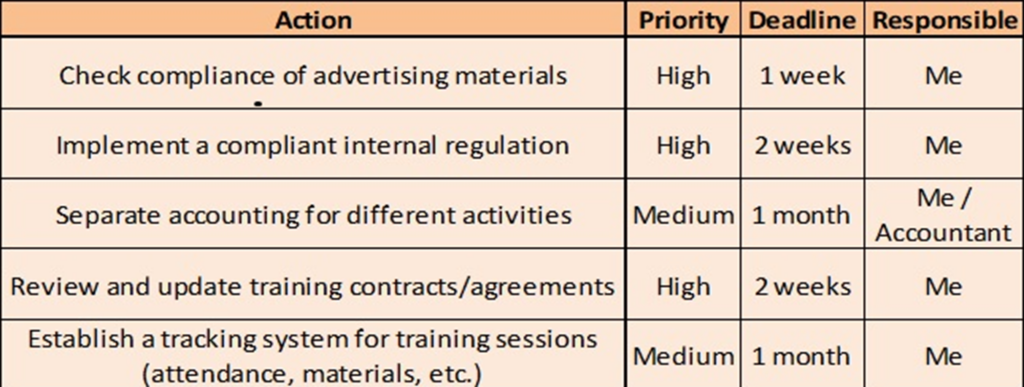
 Developing Your Compliance Roadmap
Developing Your Compliance Roadmap
 What’s at stake?
What’s at stake?
Ensuring compliance with the regulatory framework governing training organizations in France is crucial to avoid significant legal and financial penalties. Below is an overview of potential sanctions associated with each of the previously discussed non-conformities:
1. Non-compliant Advertising
Potential Sanctions:
- Financial Penalties: A fine of up to €4,500.
- Criminal Penalties: Up to one year of imprisonment.
- Operational Restrictions: Possible temporary or permanent prohibition from managing a training organization.
Legal References: Articles L.6355-16, L.6355-17, and L.6355-23 of the French Labour Code.
2. Absence of Separate Accounting
Potential Sanctions:
- Financial Penalties: A fine of up to €4,500.
- Operational Restrictions: Potential temporary or permanent ban from directing a training organization.
Legal References: Articles L.6355-10 to L.6355-14 of the French Labour Code.
3. Failure to Execute Planned Training Actions
Potential Sanctions:
- Financial Repercussions: Obligation to reimburse unduly received funds for services not rendered.
- Operational Restrictions: Possible annulment of the activity declaration, leading to a prohibition from offering training services.
Legal References: Articles L.6354-1 and L.6351-4 of the French Labour Code.
4. Absence or Non-compliance of Internal Regulations
Potential Sanctions:
- Financial Penalties: A fine of up to €4,500.
- Operational Restrictions: Potential temporary or permanent prohibition from managing a training organization.
Legal References: Articles L.6355-8, L.6355-9, and L.6355-23 of the French Labour Code.
5. Irregularities in the Nature of Services Provided
Potential Sanctions:
- Operational Restrictions: Annulment of the activity declaration if services do not align with legally defined training actions, leading to a ban on providing training services.
Legal Reference: Article L.6351-4 of the French Labour Code.
6. Insufficient Information to Trainees
Potential Sanctions:
- Financial Penalties: A fine of up to €4,500.
- Operational Restrictions: Possible temporary or permanent prohibition from managing a training organization.
Legal References: Articles L.6355-22 and L.6355-23 of the French Labour Code.
7. Non-compliance with Individual Training Contracts
Potential Sanctions:
- Financial Penalties: A fine of up to €4,500.
- Operational Restrictions: Potential temporary or permanent ban from directing a training organization.
Legal References: Articles L.6355-18 to L.6355-20 of the French Labour Code.
Important Note: Beyond these specific sanctions, non-compliance can lead to additional consequences, such as the annulment of the activity declaration, making it illegal to operate as a training provider. Moreover, failure to obtain necessary certifications, like Qualiopi, can result in the loss of access to public funding and diminish the organization’s credibility.
Given the complexity and potential severity of these sanctions, it is highly recommended to consult with legal professionals specializing in training and education law to ensure full compliance with all applicable regulations.

Thanks, this is a useful recap!